YSTIA/YORC, the LEXIS orchestration toolkit
This article provides some highlights about the orchestration technology, which is used in the LEXIS project to manage complex scientific application workloads, mixing HPC and Big Data requirements on top of a federation of heterogeneous resources.
At the basis of the LEXIS platform, the LEXIS Orchestration Service is built on a flexible orchestration solution (namely YSTIA) developed by Atos, which combines a front-end system (Alien4Cloud) and an orchestration engine (Yorc). Alien4Cloud allows to model applications using the TOSCA format, while Yorc provides large flexibility in controlling Cloud and HPC resources.
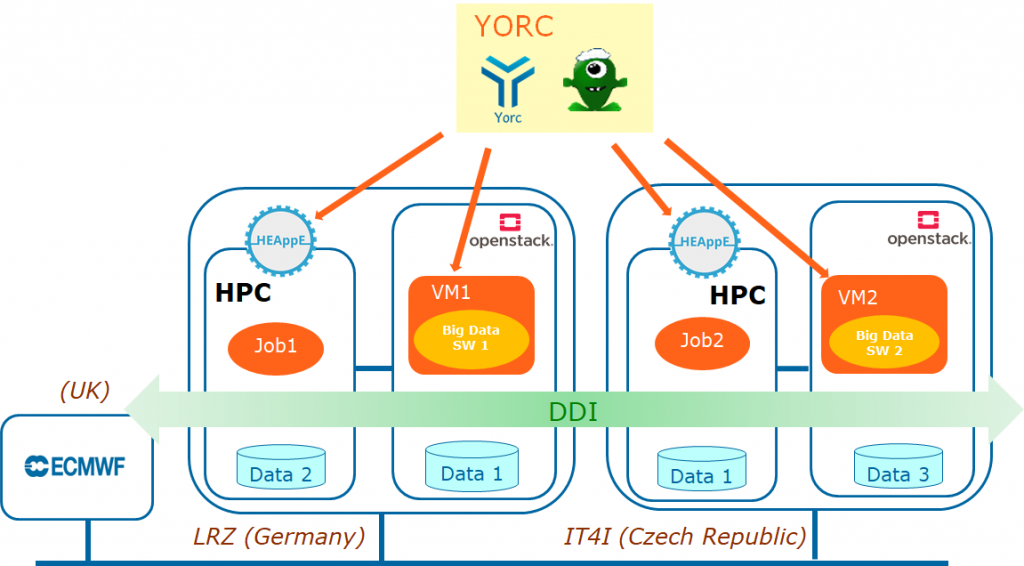
In the Figure 1 below, Yorc is used to manage workflows spanning the infrastructures available in the LEXIS project, i.e. both Cloud (OpenStack) and HPC infrastructures at LRZ and IT4I. Yorc also makes use of DDI to handle data transfers during the workflows execution.
Figure 1: Application workflow execution over several locations
The applications to be deployed are modeled using the Topology and Orchestration Specification for Cloud Applications (TOSCA [1]), an OASIS consortium standard language to describe an application made of components with their relationships, requirements, capabilities, and operations. Workflow orchestration, execution and monitoring in LEXIS relies on Yorc. Its front-end, Alien4Cloud, provides a studio allowing to create applications from an extensible catalog of TOSCA components, to deploy these applications, and to run and monitor workflows.
Both have been extended during the LEXIS project to manage the deployment and execution of workflows on multiple locations (HPC and Cloud resources on different sites), and also to properly respond to Urgent Computing constraints. Additional capabilities are being added, including dynamic capability of selecting the most suitable resources for running different tasks composing a workflow and the management of sites’ failures.
Yorc is a TOSCA native solution, it is open source, available at https://ystia.github.io/. It exposes a REST API, provides a Command Line Interface (CLI), and can be used through Alien4Cloud. Yorc is extensible through a plugin architecture, in the context of the LEXIS project, a plugin has been developed to support the HEAppE middleware [2], an intermediate framework used in the project for handling job management, monitoring and reporting, user authentication and authorization over the HPC datacenters. Yorc is also designed to use “placement policies” for dynamic resource allocation: within the LEXIS project it will be connected to a “Business Logic module” developed by the LINKS partner. Yorc provides capabilities based on TOSCA extensions to handle jobs (which is used in LEXIS for managing HPC jobs) and containers. It is developed in Go language. Although being available in Open Source, it is part of an Atos product, Atos CODEX AI Suite, which provides both the Yorc orchestration solution for hybrid deployments, and a Machine Learning toolbox called FastML, which relies on Yorc for handling Machine Learning trainings deployment on HPC infrastructures.
This orchestration technology has been used in LEXIS project to develop scientific workflows related to forest fire risk forecast, flood risk forecast, earthquake and tsunami (real time workflows to handle emergencies and disaster), Computational Fluid-Dynamic (CFD) advanced simulations in the area of aeronautical engines.
[1] https://www.oasis-open.org/committees/tc_home.php?wg_abbrev=tosca
[2] HEAppE Middleware: http://heappe.eu